Anonymous is safer


Data is a key corporate asset. The big data technologies that have emerged in recent years enable the mass storage of data, much of which is of course personal data.
However, the storage and processing of precisely this data is subject to legal requirements. The basis for this includes the German Civil Code (BGB) with its retention of title, which also applies to data, as well as special regulations in the relevant environments, such as SGB X with its requirements for patient data.
When it comes into force at the end of May 2018, the European General Data Protection Regulation (EU GDPR) with its respective national adaptations will also replace the previous Federal Data Protection Act.
As a result, this means that storing personal data is not permitted by default. However, all these regulations also define exceptions when it is permitted again.
Such an exception, as is typically implemented today, is a purpose-related consent for the fulfillment of a business relationship - for example, for the execution of an order, provision of a service, sending a newsletter.
However, the permissions quickly give the impression that this data, like other company data, can be processed almost at will. However, companies must pay very close attention to where which data is stored and processed - personal data is subject to special protection.
Personal data does not belong on the test system
The use of personal data on test and QA systems or for development systems is critical, both in the SAP and non-SAP environment. Even consent does not permit the processing of personal data there because, as described above, consent is often collected for a specific purpose.
This does not automatically include development and testing. Concepts that improve an all-round view of the customer are also all too popular in big data analytics.
This is the only way to sell customers even better products and services that are suitable for them. Of course, this requires collecting, storing and analyzing a great deal of detailed data on individuals.
Big data scenarios therefore often relate to personal data, although this is not essential. It has been proven that interesting new business models can also be developed with non-personal data.
One of the most important IT trends for 2018 will be the marketing of data by user companies. Market research company IDC, for example, has confirmed that around 90% of large companies will generate direct revenue from the sale of raw data or from insights or recommendations derived from it by 2020.
In 2017, it was still 50 percent. Data is therefore a resource that can be tapped, stored and refined. The technology for collecting, storing and refining data has been further developed in recent years - whether through cost-effective storage systems or new database concepts.
One of the most important tasks for IT managers and those responsible for digital transformation will therefore be to put the marketing of their own data on the right track.
The capitalization of data is all the rage. However, due to the aforementioned legal provisions, this may only be personal data in rare cases.
Anonymize or delete?
There are no problems with the capitalization of information with anonymized data. Libelle AG from Stuttgart, previously known for its solutions for the high availability of SAP and non-SAP databases and SAP and non-SAP system copies, has further developed its expertise in these two areas and, with Libelle DataMasking (LDM), has developed a solution for the necessary anonymization and pseudonymization.
The solution was designed to produce anonymized, logically consistent data on development, test and QA systems across all platforms. The anonymization methods used provide realistic, logically correct values that can be used to describe almost all business cases and test them end-to-end in a meaningful way.
Pseudonymization and anonymization are among the approaches used to handle critical data, especially personal data, before it is passed on or processed further. However, good anonymization can be more difficult than it seems at first glance.
One simple option is to delete or overwrite critical real data on the non-productive systems. However, the individual data records lose their logical connections and dependencies to each other - and therefore their useful value.
Pseudonymization
Pseudonymization involves replacing real data with false data, usually simple numerical values. However, it is often not enough to replace the surname, first name and date of birth or similar with incorrect values in the customer database, for example.
A simple comparison of such databases with publicly accessible telephone directories is often sufficient to restore the personal reference. For this reason, special high-quality anonymization procedures should be used.
Libelle DataMasking is a solution for the automated processing of sensitive data. It allows data of any complexity to be handled using comprehensive anonymization methods.
Preconfigured functions can be quickly and easily applied to data fields that have been identified as critical and sensitive. Specialist and/or technical managers can thus fall back on standardized rules and also set up rules of any complexity with which, for example, highly structured and meaningful data types can be calculated.
Clean data for development and testing
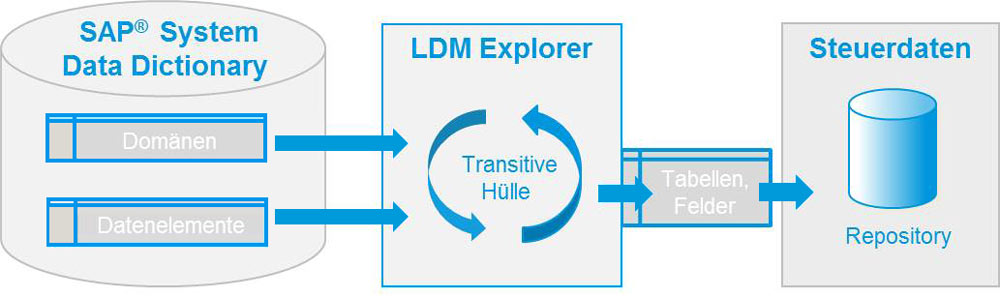
It is not always clear to application administrators and programmers which data actually belongs to the sensitive data. A central component of Libelle's anonymization solution is the LDM Explorer for one-off or, after structural changes, recurring analysis of databases and file systems and their respective data models for content to be anonymized.
The responsible persons check, verify and, if necessary, supplement the results of the LDM Explorer in order to then link them to typical anonymization procedures using the LDM Associator.
This forms the basis for automatic, logically consistent and consistent anonymization of related data records across system boundaries. LDM currently offers 75 standardized anonymization profiles for standard situations.
Once the data has been identified and linked to the corresponding anonymization procedures, the operational anonymization steps of the LDM take effect. In addition to company-specific special cases, these then handle name fields, address information, bank data and data such as date of birth and order date out of the box. Indices are also rebuilt, if affected.
Further scenarios
This provides developers and users with a "clean" database that means they don't have to worry about data protection. Many other application scenarios for Libelle DataMasking are conceivable - including the examples mentioned at the beginning for the transfer of anonymized data as part of a supply chain, in the context of an open data pool or for commercial marketing.