On New Paths to Holistic SAP Modernization: Navigation System


An entrepreneurial structure and process organization should overcome silos and achieve cross-functional end-to-end processes. The foundation for this is provided by open-source technologies and open source-based certified enterprise Kubernetes platforms and automation solutions.
The SAP world is changing—away from the classic ECC 6.0 to a new application landscape with the digital core in S/4 Hana as well as new services and frameworks. This means that SAP modernization is not simply a regular, routine upgrade. In addition to the 2027 deadline for migrating databases to SAP Hana and applications to S/4, there are several other challenges to address. These include the essential modernization of specialized applications and in-house developments with a cloud-ready or cloud-first approach, the implementation of automation to bridge organizational silos, the integration of modern solutions into daily operational processes, and the incorporation of SAP's innovation roadmap featuring cloud solutions like S/4 or RISE.
The migration itself presents a challenge tasks, particularly when dealing with legacy systems, outdated solutions, non-cloud-enabled interfaces, and integrations designed solely for on-premises use. Instances of these challenges include backup and monitoring tools or Abap-based add-ons from the ECC landscape.
The changes are in the context of digital transformation, which is essential for almost every company. To remain competitive in the process, modern IT environments must be able to implement new ideas or additional functions agilely and at high speed. Agility also means being able to react immediately to failures, changing market and user requirements and unforeseeable situations—and this also applies to the SAP world.
Being locked into a particular solution is counterproductive; in essence, every company requires long-term strategic adaptability in this context. This is growing in significance, especially due to regulatory requirements. The regulation affects all types of financial companies, from credit institutions to insurance companies, investment firms, and all third-party providers of information and communication technologies that provide services to the financial services sector.
Through the new regulation, the EU is addressing the growing digitalization of the financial sector and the accompanying elevated security risks, including concerns related to the concentration of data in the cloud. This entails that companies should reduce their IT and business-critical risks while enhancing their operational resilience. In this regard, open source-based solutions, known for their consistent avoidance of vendor lock-in and their emphasis on independence and interoperability, are growing in significance.
The essential transformation within the SAP landscape primarily demands the seamless integration of new applications, technologies, platforms, architectures, and frameworks. This includes areas like AI and ML, data analytics, big data, RPA, and IoT. Notably, AI and ML are currently gaining significant importance, especially among SAP users. Many companies are actively developing and training models using SAP data, subsequently deploying them in production environments, such as factory and edge scenarios.
Hybrid cloud as target architecture
The different requirements raise the question of the optimal target architecture and basis for implementing concepts that link migration scenarios with modernization and innovation topics. The solution lies in open-source technologies, cloud-native development approaches involving containers and microservices, certified enterprise Kubernetes platforms, and automation solutions, specifically Red Hat OpenShift and Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform. It's precisely this infrastructure that an increasing number of SAP partners, tools, and solutions are opting to integrate the SAP landscape into a more agile process environment.
SAP itself is also increasingly taking this path and relying on solutions from Red Hat. The two companies announced an intensified partnership at the beginning of the year. Within the framework of this partnership, SAP is gradually migrating an ever larger part of its internal IT landscape and its SAP Enterprise Cloud Services portfolio to the standardized base of Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
That is, SAP is also primarily using Red Hat as the foundation for new SAP RISE customer environments. This joint initiative to extend SAP software workloads on Red Hat Enterprise Linux is designed to make it easier for SAP customers to increase business agility, accelerate cloud deployments, and drive business innovation by building on Red Hat's scalable, flexible, and open hybrid cloud infrastructure.
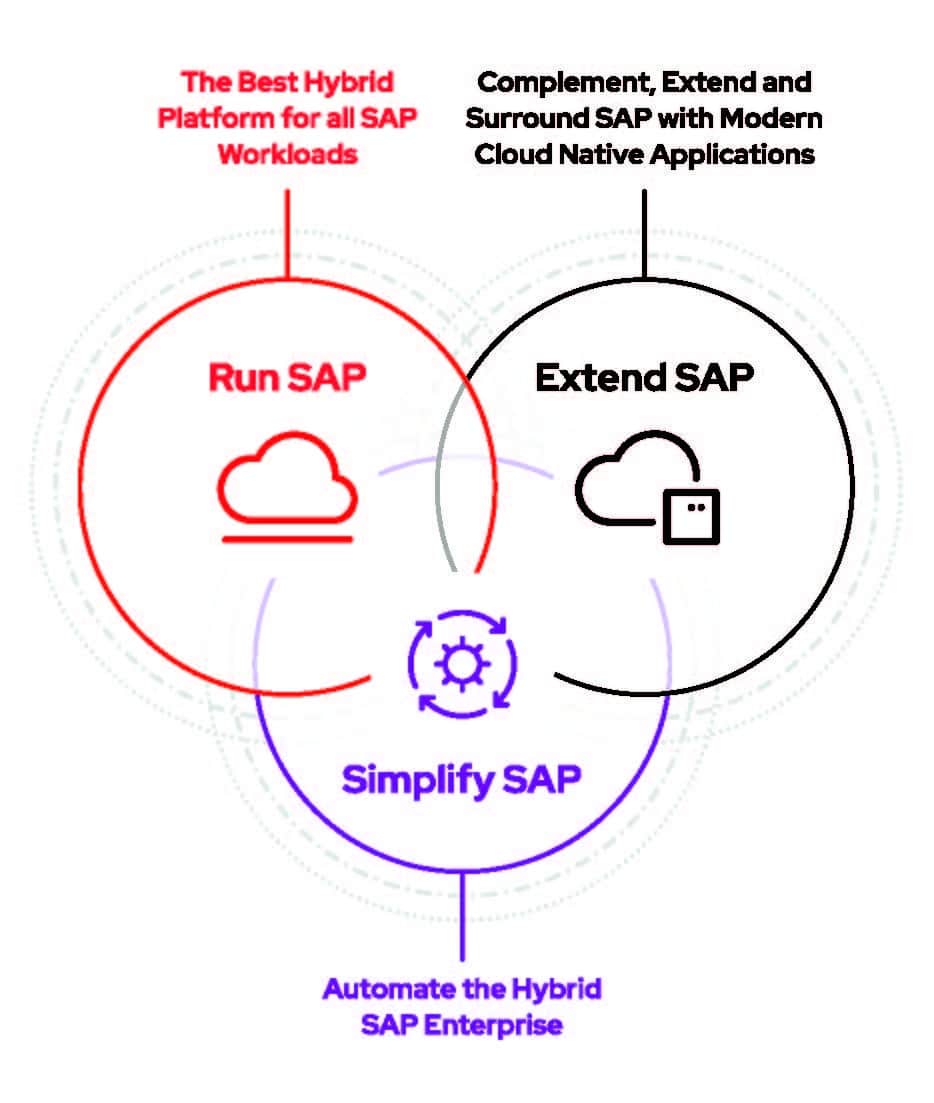
Holistic approach to SAP modernizations.
Open source-based hybrid cloud platforms and integrated end-to-end architectures are pivotal components for the success of SAP migration and modernization. Automation serves as a central link and plays a crucial role. Today, it stands as one of the central themes in the world of IT, including within the SAP domain. To tackle both present and future challenges during this era of digital transformation, companies must embrace automation that extends beyond simple deployment, reaching into comprehensive end-to-end automation of the entire process landscape. This entails automation spanning from deployment through maintenance to the operation of the entire IT stack. The versatile and established open source automation solution, Ansible, provides invaluable support in this regard. For enterprise-grade usage, the Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform has proven itself, offering certified, preconfigured modules, automation workflows, and advanced security concepts that enable seamless scaling across various domains a
Automation as a bridge builder
Open source-based hybrid cloud platforms and integrated end-to-end architectures are key success components of SAP migration and modernization. A central link and important bridge builder is automation. Today, it is one of the central IT topics, also in the SAP world. Current and future challenges in a time of digital transformation can only be mastered by companies with automation that goes beyond pure deployment in the direction of consistent end-to-end automation of the entire process landscape. This means that automation must extend from deployment through maintenance to the operation of a complete IT stack. The universal and proven open source automation solution Ansible provides crucial support in this regard. For enterprise use, Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform has established itself: Certified, preconfigured modules, automation workflows, and advanced security concepts allow cross-domain scaling across silos.
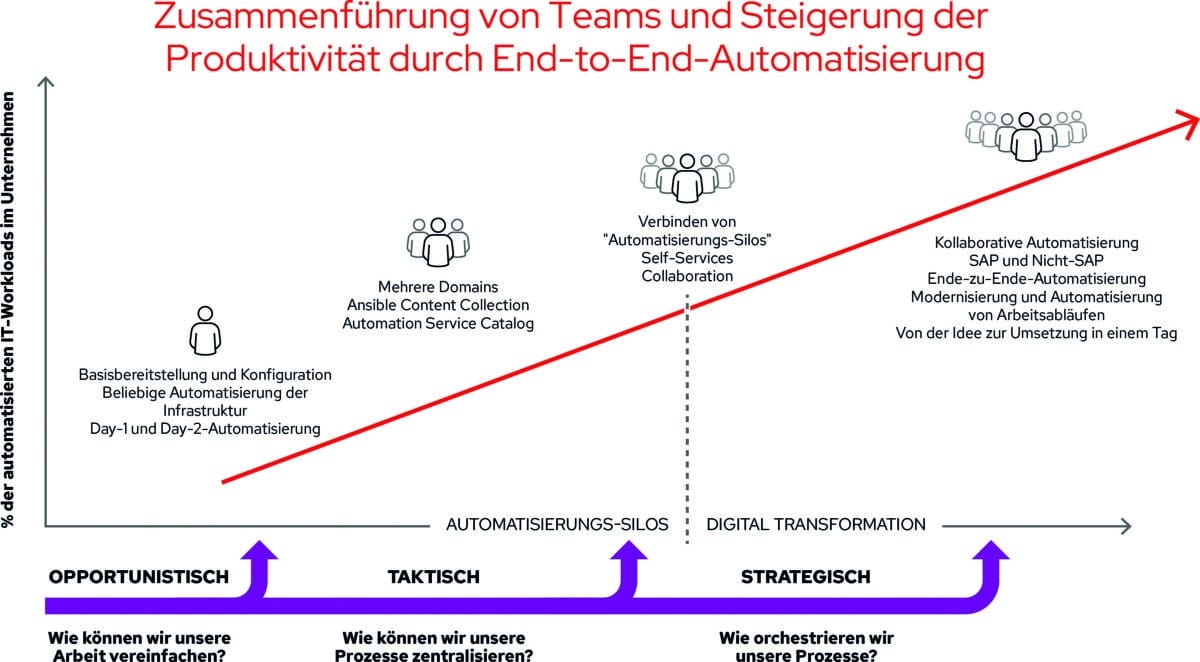
Bring teams together and increase productivity through end-to-end automation.
Tactical and strategic
An effective strategy for deploying Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform enterprise-wide involves a phased approach. It typically commences with an opportunistic approach, progresses to a tactical one, and finally to a strategic deployment. This entails starting by simplifying individual processes, then centralizing automation procedures, and finally orchestrating entire automation workflows. SAP landscapes have now seamlessly integrated into this overarching strategy.
The potential spectrum of Ansible deployment within the SAP context is extensive. On one hand, it encompasses infrastructure and maintenance tasks related to deployment, installation, and provisioning. On the other hand, it involves "housekeeping" activities within ongoing SAP operations, which includes automating processes within SAP applications. Extensions from the partner ecosystem facilitate direct automation in SAP through Ansible, such as managing rights, creating users, reading system data, or even executing processes.
The use cases that Ansible covers are continuously increasing. Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform, for example, currently has more than 130 certified and maintained content collections that are developed and provided by hardware and software manufacturers and Red Hat, and with regards to automation in SAP environments. According to Red Hat's experience, the Content Collections provide use cases for about 80 percent of typical application scenarios, while ensuring easy customization to meet specific customer and requirements.
In addition, the flexibility of Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform enables SAP users to easily integrate automation with existing tools and processes using RESTful APIs and a self-service portal. For example, they can address issues such as compliance, security and governance that traditionally require a great deal of manual effort. Automation eliminates this effort and also supports, for instance, faster implementation of the new supply chain due diligence law by seamlessly connecting different data sources.
SAP RISE
One might begin to question whether the hybrid cloud serves as a viable alternative to SAP RISE and whether, in any case, RISE by itself represents a comprehensive and all-encompassing solution. However, it is not a question of replacing RISE or the SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP), but of integrating and balancing an outside-in and inside-out view of processes. There are several reasons for this. First, it should be noted that SAP users receive many pre-integrated and useful extensions for SAP processes thanks to the BTP. In addition, an open hybrid cloud as an often already established foundation in the customer's IT landscape offers users the necessary and desired flexibility in terms of development and operation. The key to success lies in the connection. With Red Hat OpenShift, for example, an abstraction and integration layer is available for hyperscaler platforms with their native services as well as for the SAP-BTP environment.
SAP and Non-SAP
Due to various factors like functional, technical, business, or compliance considerations, SAP Rise may not be well-suited for all non-SAP workloads. This is particularly evident in cases involving security requirements, such as in public and military contexts, as well as edge application scenarios. In contrast, a cloud-native runtime environment as a foundation supports a wide range of environments, including hybrid, on-premises, and edge environments, thereby accommodating diverse customer-specific and application-specific requirements.
Overall, every migration and modernization project in the SAP area should be seen in the context of a redesign and consolidation of the entire IT landscape. The ideal technological foundations for this are certified open source-based operating systems, hybrid cloud platforms, and automation solutions such as Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Red Hat OpenShift, and Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform. It is no coincidence that more and more partners from the SAP ecosystem are using precisely this technology substructure for SAP modernizations as an integrated open source-based toolchain. The rationale behind this is quite compelling: there is a substantial room for enhancement in terms of how SAP modernizations and migrations are calculated, streamlined, and expedited.








